Table of Contents
Opening smart water devices requires careful consideration and adherence to safety guidelines. Here are key steps to open smart water devices like a pro:
Read the Manual
Reading the manual is a fundamental and crucial step when dealing with any electronic device, including smart water devices. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of what this step entails:
Locate the Manual
Find the user manual or documentation that came with the smart water device. This could be a physical booklet included in the packaging or a digital version available on the manufacturer’s website.
Thoroughly Review Content
Take the time to thoroughly review the manual. Pay attention to sections related to device specifications, safety precautions, and user guidelines. Important information about opening, maintenance, and troubleshooting may be included.
Understand Device Features
Familiarize yourself with the features and functions of the smart water device. Understanding how it works and its various components will give you a better context when opening it.
Check for Warnings and Cautions
Look for any warnings, cautions, or specific instructions related to disassembly or opening the device. Manufacturers often provide important information to prevent damage or injuries.
Identify Tools and Accessories
The manual typically mentions the tools and accessories required for tasks such as opening the device, replacing components, or performing maintenance. Make a list of these tools before starting.
Follow Manufacturer’s Recommendations
Manufacturers may provide specific recommendations for handling the device. This could include temperature ranges, humidity levels, or other environmental conditions. Adhering to these recommendations ensures optimal device performance and longevity.
Note Maintenance Intervals
Some manuals provide information about regular maintenance intervals. If applicable, take note of any recommended maintenance schedules and follow them to keep the device in good working condition.
Warranty Information
Check the warranty information provided in the manual. Opening the device in a way that violates the terms of the warranty may void it. If you’re unsure, consult the warranty section or contact the manufacturer for clarification.
Troubleshooting Section
The troubleshooting section of the manual can be a valuable resource. It often contains solutions to common issues, which can guide you in diagnosing problems without the need for opening the device.
Contact Information
Take note of the manufacturer’s contact information, including customer support channels. If you have questions or encounter difficulties, reaching out to the manufacturer can provide helpful guidance.
Power Off
The “Power Off” step is crucial when dealing with any electronic device, including smart water devices. Here’s a detailed explanation of what this step involves:
Locate Power Source
Identify the power source of the smart water device. This could include batteries, electrical outlets, or any other power supply.
Disconnect Power Source
Safely disconnect the device from its power source. If the device is battery-powered, remove the batteries. If it’s connected to an electrical outlet, unplug the power cord.
Turn Off Switches
If the smart water device has any power switches or controls, turn them off. This ensures that no electrical current is flowing through the device during the opening process.
Wait for Shutdown (if applicable)
If the device has a built-in shutdown process, allow it to complete before proceeding. Some devices may have internal processes that need to finish before it’s safe to disconnect the power.
Check for Indicators
Confirm that any power indicators or lights on the device are turned off. This visual confirmation ensures that power has been successfully cut off.
Wait for Capacitor Discharge (if applicable)
In some electronic devices, capacitors can store electrical charge even after the power is turned off. Consult the manual or follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure safe discharge if applicable.
Verify Power Off (Multifunction Devices)
For multifunction devices, ensure that all functions (such as printing, scanning, etc.) are fully stopped before proceeding with the power-off step.
Ensure Safety of Connected Components
If the smart water device is part of a larger system or connected to other equipment, ensure that those components are also powered off or disconnected to prevent any unintended interactions.
Consider Environmental Factors
Take note of the environment where you are working. If the smart water device is in an area with potential electrical hazards (such as wet conditions), take appropriate precautions.
Follow Emergency Procedures (if necessary)
In critical situations or emergencies, refer to any emergency procedures outlined in the manual. This may include specific steps to follow when powering off the device under unusual circumstances.
Use the Right Tools
Using the right tools is essential for safely and effectively opening smart water devices. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what this step involves:
Refer to the Manual
Check the user manual or documentation for information on the tools recommended by the manufacturer. The manual may specify the types and sizes of tools required for opening the device.
Identify Necessary Tools
Determine the specific tools needed for disassembly. Common tools for opening electronic devices include screwdrivers, pliers, tweezers, and prying tools. Specialized tools may be required for certain devices.
Quality Tools
Ensure that the tools you use are of high quality. Cheap or improperly sized tools can cause damage to screws, components, or the device casing. Invest in tools that are appropriate for electronic device disassembly.
Magnetic Screwdriver or Mat
A magnetic screwdriver or mat can be useful for keeping track of small screws and preventing them from getting lost during the disassembly process.
ESD-Safe Tools (if applicable)
If you’re dealing with electronic components, especially in smart devices, consider using Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)-safe tools. ESD can damage sensitive electronic components, so using ESD-safe tools helps prevent this.
Prying Tools and Spudgers
For devices with sealed edges or clips, prying tools and spudgers can be handy. They help open the casing without causing damage. Plastic tools are often preferred to avoid scratching the device.
Anti-Static Wrist Strap
If you’re working with internal electronic components, consider using an anti-static wrist strap to ground yourself and prevent electrostatic discharge. This is especially important in dry or low-humidity environments.
Precision Screwdrivers
Devices often have small screws that require precision screwdrivers. Ensure you have the right size and type of screwdriver for the screws used in the device.
Organizational Tools
Use containers, trays, or magnetic mats to organize and keep track of screws and small components. Labeling or taking pictures of the disassembly process can help during reassembly.
Gloves and Safety Glasses
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses, to protect yourself from sharp edges and potential hazards inside the device.
Non-conductive Tools (if necessary)
In cases where you are working with live electrical components, use non-conductive tools to reduce the risk of electrical shock.
Avoid Excessive Force
Use the right amount of force when using tools. Excessive force can lead to damage. If something seems stuck, recheck the manual or seek guidance before applying more force.
Inspect Tools Before Use
Before starting, inspect your tools to ensure they are in good condition. Damaged tools can cause accidents or damage to the device.
Safety Gear:
Safety gear is crucial when working with any electronic device, including smart water devices. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the safety gear you should consider using:
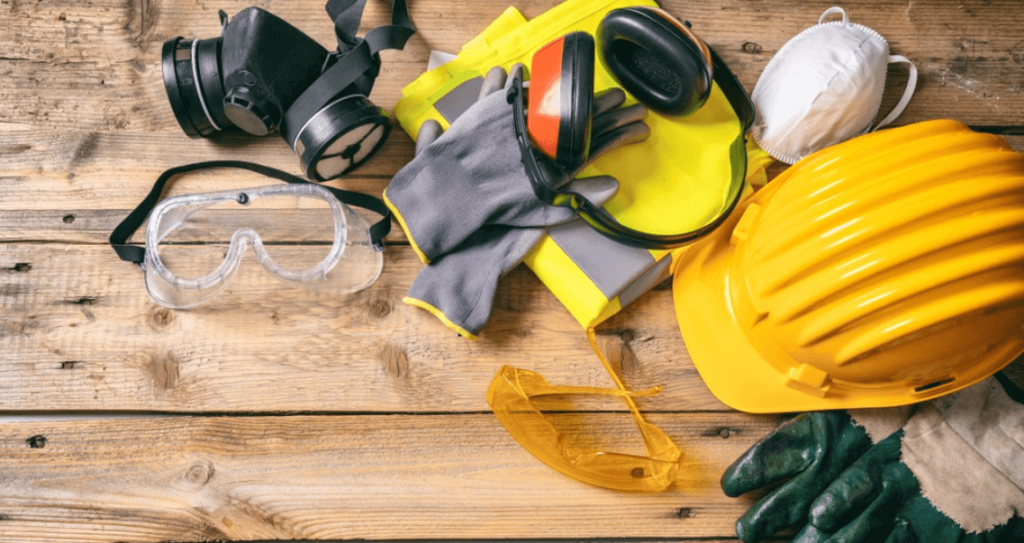

Gloves
Wear appropriate gloves to protect your hands from sharp edges, potential electrical contacts, or any chemicals that might be present inside the device. Choose gloves that are comfortable and allow for dexterity to handle tools effectively.
Safety Glasses or Goggles
Protect your eyes from dust, debris, or any small components that may be dislodged during the opening process. Safety glasses or goggles with side shields are recommended.
Anti-Static Wrist Strap
If you’re working with internal electronic components, especially in devices that are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD), use an anti-static wrist strap. This helps prevent ESD-related damage by grounding you.
ESD-Safe Mat
Work on an ESD-safe mat, especially if you are dealing with electronic components. This helps dissipate static electricity and protects sensitive components from damage.
Appropriate Clothing
Wear clothing that covers your arms and legs to protect against accidental contact with sharp edges or components. Avoid loose clothing that could get caught on tools or inside the device.
Closed-Toe Shoes
Wear closed-toe shoes to protect your feet from potential hazards, especially if you’re working in an environment where dropped tools or components may pose a risk.
Respirator Mask (if necessary)
If there is a risk of exposure to dust, fumes, or other airborne particles, use a respirator mask to protect your respiratory system. This is particularly important if you’re working with materials that may be harmful when inhaled.
Hair Restraints
If you have long hair, tie it back or use a hair restraint to prevent it from getting caught in tools or components.
First Aid Kit
Keep a basic first aid kit nearby in case of minor injuries. It should include bandages, antiseptic wipes, and any necessary personal medications.
Fire Extinguisher (if applicable)
In some work environments, especially those with potential fire hazards, have a fire extinguisher nearby and ensure you know how to use it.
Emergency Contact Information
Have emergency contact information readily available in case of an accident or injury. This may include contact numbers for local emergency services, as well as any workplace-specific emergency procedures.
Safety Training
Ensure you have received appropriate safety training, especially if you are working in a professional setting. Understand the specific safety protocols and guidelines for your work environment.
Ventilation
If you’re working with materials that produce fumes, ensure good ventilation in the workspace. Open windows or use fans to minimize exposure to potentially harmful substances.
Identify Seals and Latches
Identifying seals and latches is an essential step when opening smart water devices. Seals and latches are designed to secure the device and protect it from external elements. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what this step involves:
Examine the Device Exterior
Carefully inspect the exterior of the smart water device. Look for any visible seams, edges, or access points where seals or latches might be present.
Refer to the Manual
Check the user manual or documentation for information about the location of seals and latches. The manual may provide specific guidance on how to access internal components and where to find these securing mechanisms.
Look for Gaskets or Rubber Seals
Water-resistant or waterproof devices often have gaskets or rubber seals around seams and openings. Inspect these areas for any signs of seals that may need to be broken to access the interior.
Check for Screws
Screws are common fasteners used in electronic devices. Examine the exterior for visible screws, as these may indicate access points. Refer to the manual for information on the types of screws used and the correct tools for removal.
Identify Clips or Latches
Some devices use plastic clips or latches to secure the casing. These are often located along the edges. Use a plastic prying tool or spudger to gently release these clips without causing damage.
Inspect for Tamper-Evident Seals (if applicable)
In certain devices, especially those that require a high level of security or have warranty restrictions, tamper-evident seals may be present. Breaking these seals may void warranties or indicate unauthorized access.
Consider Heat Seals (if applicable)
In some cases, heat seals may be used to secure the casing. Heat may need to be applied to soften the adhesive before attempting to open the device. Ensure you follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for this process.
Check for Hidden Screws or Fasteners
Some devices may have screws or fasteners hidden under labels, rubber feet, or decorative covers. Carefully inspect these areas to uncover hidden securing mechanisms.
Use a Flashlight
In dimly lit environments, use a flashlight to enhance visibility and identify any hidden seals, latches, or screws.
Be Mindful of Water Resistance
If the smart water device is designed to be water-resistant, be cautious when breaking seals. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to maintain water resistance after reassembly.
Document the Seal and Latch Locations
As you identify seals and latches, take notes or pictures to document their locations. This documentation will be useful during the reassembly process.
Avoid Excessive Force
Use gentle pressure when attempting to open the device. Excessive force can damage seals, latches, or the device casing. If you encounter resistance, recheck for any missed securing mechanisms.
Document the Process
Documenting the process of opening a smart water device is crucial for several reasons, including aiding in reassembly and troubleshooting. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what this step involves:
Prepare Note-Taking Tools
Before you begin, gather tools for note-taking, such as a notepad, pen, or a digital device for taking pictures. Ensure these tools are readily accessible during the disassembly process.
Take Pictures
Use a camera or smartphone to take clear pictures of the smart water device before and during the disassembly. Capture the external components, internal wiring, and the arrangement of parts. These pictures will serve as visual references during reassembly.
Label Components
If you need to remove specific components, label them with sticky notes or use a marker to indicate their positions. This is particularly important if components are similar but have distinct orientations.
Draw Diagrams
Create simple diagrams or sketches to illustrate the arrangement of internal components, their connections, and any cables or wires. This can be helpful in understanding the device’s internal structure.
Note Screw Locations
Record the locations and types of screws as you remove them. Use labels or a diagram to indicate where each screw belongs. This ensures that you can reassemble the device correctly.
Document Cable Connections
If the smart water device has cables connecting various components, document the connections. Note the colors and positions of the cables, and consider labeling them to avoid confusion during reassembly.
Record Disassembly Steps
Write down the steps you take during the disassembly process. Include details on how you removed specific components, any challenges encountered, and solutions applied. This information can be valuable for troubleshooting later.
Note the Order of Removal
If components need to be reinstalled in a specific order, document the sequence in which you removed them. This ensures that you can reverse the process during reassembly.
Record Serial Numbers and Model Information
Make a note of the device’s serial number, model information, and any other identification details. This information may be needed for warranty purposes or when seeking technical support.
Include Timestamps
Timestamp your notes or pictures to create a chronological record of the disassembly process. This can be useful for tracking the time spent on each step and understanding the overall timeline.
Note Special Instructions
If you encounter any special instructions or peculiarities during the disassembly, document them. This information may be critical for troubleshooting or providing context during reassembly.
Store Documentation Safely
Keep your notes, pictures, and diagrams in a safe and organized manner. Storing them digitally can help ensure easy access when needed.
Antistatic Precautions (if applicable)
Antistatic precautions are essential when working with electronic devices, including smart water devices. These precautions help prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) that could potentially damage sensitive electronic components. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to take antistatic precautions:
Understand the Risk of ESD
Electrostatic discharge occurs when an imbalance of static electricity is released, and it can damage or destroy electronic components. Smart water devices often contain sensitive electronic circuits, making them susceptible to ESD.
Wear an Antistatic Wrist Strap
Before handling the smart water device, put on an antistatic wrist strap. This strap typically has a conductive material that grounds you, allowing any built-up static charge to dissipate harmlessly.
Attach the Wrist Strap Properly
Attach one end of the antistatic wrist strap to your wrist and the other end to a grounded point, such as the grounding pin of an electrical outlet or a designated grounding mat. Ensure that the strap is snug but not too tight.
Use an Antistatic Mat (if available)
If you have access to an antistatic mat, place it on your work surface. Connect the mat to the same grounding point as the wrist strap. This provides a controlled, antistatic work environment.
Handle Components Carefully
When handling electronic components or circuit boards, avoid touching sensitive areas, such as pins or connectors. Hold them by their edges to minimize the risk of ESD.
Avoid Synthetic Clothing
Synthetic fabrics can generate static electricity. If possible, wear clothing made of natural fibers like cotton, which tends to produce less static.
Work in a Controlled Environment
Minimize environmental factors that contribute to static electricity. Keep the humidity level in your workspace within the recommended range (typically 40-60%) to reduce the risk of ESD.
Ground Yourself Before Touching Components
Before touching any electronic components or opening the smart water device, touch a grounded metal object to discharge any static electricity accumulated on your body.
Use ESD-Safe Tools
If available, use tools that are specifically designed to be ESD-safe. These tools typically have antistatic coatings or materials to minimize the risk of static discharge.
Store Components in Antistatic Bags
When not in use, store electronic components in antistatic bags. These bags are designed to prevent the buildup of static electricity and protect components during storage and transportation.
Be Mindful of Movement
Move slowly and deliberately, especially in environments prone to static buildup. Quick movements can generate static electricity.
Avoid Work During Dry Conditions
ESD risks are higher in dry conditions. If possible, avoid working on electronic devices during excessively dry weather.
Follow Disassembly Steps
Following the disassembly steps carefully is crucial to avoid damage to the smart water device and to ensure a successful opening process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Refer to the User Manual
Start by thoroughly reading the user manual or documentation provided by the manufacturer. Look for specific disassembly instructions, warnings, and precautions.
Gather Necessary Tools
Collect all the tools needed for disassembly based on the information in the manual. Ensure you have the right screwdrivers, pliers, prying tools, and any other tools specified.
Power Off the Device
Ensure the smart water device is powered off and disconnected from any power sources. This is a critical safety step before beginning the disassembly process.
Wear Safety Gear
Put on the necessary safety gear, including gloves and safety glasses, to protect yourself from potential hazards during disassembly.
Ground Yourself
If you are working with electronic components, wear an antistatic wrist strap and connect it to a grounded point. This helps prevent electrostatic discharge that could damage sensitive components.
Identify Seals and Latches
Identify and address any seals, latches, or securing mechanisms as outlined in the manual. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for breaking seals without causing damage.
Document the Starting Point
Take a picture or make a note of the initial state of the device before you start disassembly. This serves as a reference point for reassembly.
Follow Sequential Steps
Carefully follow the disassembly steps provided in the manual. The steps may include removing screws in a specific order, releasing clips, or detaching connectors. Adhere to the recommended sequence to avoid complications.
Document as You Go
Take pictures or make notes at each step. Document the location and type of screws, connections between components, and any special instructions provided in the manual.
Use the Right Amount of Force
Apply gentle and controlled force when required. If something seems stuck, refer to the manual for guidance before applying more force to avoid damage.
Organize Removed Components
Place removed screws and components in an organized manner. Use containers or labeling to keep track of small parts. This will simplify the reassembly process.
Inspect Components for Damage
As you disassemble, inspect components for any signs of damage or wear. Document any issues you observe.
Follow Safety Guidelines
Adhere to safety guidelines outlined in the manual. Avoid shortcuts or skipping steps, as this can lead to complications during reassembly.
Work in a Clean Area
Keep your workspace clean to avoid foreign particles entering the device. Work on a clean surface and handle components with care.
Pause and Double-Check
Periodically pause during the disassembly process to double-check your progress against the manual. Confirm that you are following the correct steps and haven’t missed any details.
Inspect for Damage
Inspecting for damage during the disassembly process is crucial to identify any issues that may need attention or repair. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to inspect for damage:
Document Initial State
Before starting the disassembly, take pictures or make notes about the initial state of the smart water device. This serves as a reference point for identifying any changes or damage.
Inspect External Components
As you disassemble the device, inspect the external components, such as the casing, buttons, and displays. Look for scratches, dents, or any visible damage. Document any issues you observe.
Check for Water Damage:
If the smart water device is water-resistant or waterproof, inspect for any signs of water damage. Look for moisture, discoloration, or corrosion. Document your findings.
Examine Seals and Gaskets:
Inspect the seals, gaskets, or rubber components that contribute to the device’s water resistance. Check for any wear, tears, or damage that could compromise the integrity of these seals.
Inspect Connectors and Cables:
Examine connectors and cables for any signs of damage, such as bent pins, frayed wires, or loose connections. Document the condition of each component.
Check for Bent or Damaged Pins
If the device has connectors with pins, carefully inspect them for any bending, misalignment, or damage. Damaged pins can affect the connectivity of components.
Inspect Circuit Boards
If you have access to the internal circuit boards, visually inspect them for any signs of damage, such as burnt areas, damaged traces, or loose components.
Look for Corrosion
Check for any corrosion on metal components, connectors, or circuitry. Corrosion can result from exposure to moisture or other environmental factors.
Inspect Screws and Fasteners
Examine the screws and fasteners you removed during disassembly. Check for any stripped threads, corrosion, or damage that may affect their functionality.
Document Findings
Document any damage or issues you identify during the inspection. Include details such as the location and extent of the damage.
Compare with Initial Documentation
Compare your findings with the initial documentation you created before starting the disassembly. Note any discrepancies or unexpected changes.
Identify Potential Causes
Try to identify the potential causes of any damage you find. Was it present before the disassembly, or did it occur during the process? Understanding the cause can help in addressing the issue.
Consider Reassembly Implications
Evaluate how the identified damage may impact the reassembly process. Determine whether repairs or replacements are necessary before proceeding.
Consult Manufacturer Guidelines
If you encounter damage and are unsure of the appropriate course of action, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek advice from their customer support.
Plan for Repairs or Replacement
Based on your inspection findings, plan for any necessary repairs or component replacements. Ensure you have the required tools and replacement parts before continuing.
Work in a Clean Area
Working in a clean area is crucial when opening and handling smart water devices to prevent contamination and ensure the integrity of internal components. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to maintain a clean work area:
Clear and Clean Workspace
Clear your workspace of unnecessary items to create a clean and organized environment. Remove any debris, papers, or unrelated tools to minimize the risk of contamination.
Use a Clean Work Surface
Choose a clean and flat work surface for disassembling the smart water device. Avoid surfaces that may introduce dust, dirt, or other contaminants to the device.
Wash Hands and Wear Clean Clothing
Before starting the disassembly process, wash your hands thoroughly to remove any oils or contaminants. Wear clean clothing to minimize the transfer of dirt or lint to the device.
Clean Tools
Ensure that all tools you plan to use are clean and free of dirt, grease, or residue. Wipe down tools with a clean cloth before starting the disassembly.
Use Antistatic Mat (if available)
If you have access to an antistatic mat, use it to create a controlled work environment. An antistatic mat helps prevent electrostatic discharge and provides a clean surface for your work.
Organize Components
Use containers, trays, or magnetic mats to organize and store screws and small components as you remove them. Labeling containers can help you keep track of different parts.
Limit Movement in the Workspace
Minimize unnecessary movement in the workspace to prevent the introduction of dust or contaminants. Move deliberately and avoid creating air currents that could disperse particles.
Avoid Consuming Food and Beverages
Refrain from eating or drinking in the workspace to prevent crumbs, spills, or other potential sources of contamination. Keep food and drinks in a designated area away from the work surface.
Close Doors and Windows
If possible, close doors and windows to minimize the entry of external dust or debris. Controlling the airflow in the workspace contributes to a cleaner environment.
Clean the Device Exterior
Before opening the device, wipe down the exterior with a clean, lint-free cloth. This helps remove any surface dust or particles that could enter the device during disassembly.
Use Compressed Air (if necessary)
If there are small crevices or openings in the device, use compressed air to blow away dust or debris. Hold the device in a way that prevents blown particles from re-entering.
Replace Cleaning Materials as Needed
If you use cleaning materials such as cloths, ensure they are clean and free of debris. Replace them as needed to maintain a clean working environment.
Be Mindful of Environmental Conditions
Consider the environmental conditions of the workspace. Avoid working in areas with high levels of dust, humidity, or other factors that could compromise cleanliness.
Re-Clean if Necessary
If you notice any contamination during the disassembly process, pause and clean affected areas before proceeding. This prevents contaminants from entering the device.
Keep Track of Screws and Parts
Keeping track of screws and parts is essential to ensure a smooth reassembly process and avoid complications. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to effectively manage and organize screws and parts during the disassembly of a smart water device:
Use Containers or Magnetic Mats
Place small containers, trays, or magnetic mats on your work surface to organize and store screws and small parts. These containers will prevent screws from rolling away and getting lost.
Label Containers
Label each container or section of the magnetic mat to correspond with specific components or steps in the disassembly process. This helps you easily identify and locate the screws during reassembly.
Separate Screws by Size and Type
As you remove screws, categorize them by size and type. Keep screws that are similar in size and shape together to avoid confusion during reassembly. Use separate containers for different components.
Document Screw Locations
Take pictures or make notes to document the locations of screws as you remove them. Note any variations in size or type. This documentation will serve as a reference during reassembly.
Use Color-Coding (if applicable)
If you have multiple types of screws, consider using color-coded containers or labels to distinguish between them. This can be particularly useful when dealing with screws of similar sizes.
Keep Screws with Removed Components
If a component has multiple screws, keep the screws with the component they belong to. Place them in a container or bag attached to the component. This maintains the association between screws and parts.
Bagging Method
Use small resealable plastic bags to group screws and parts. Label each bag with the corresponding component or step in the disassembly process. This method helps prevent mixing and misplacement.
Write Down Details
If you encounter screws with specific characteristics or if certain screws need special attention during reassembly, make notes or mark the containers accordingly.
Be Methodical
Remove screws in a systematic and methodical manner. Follow a specific order outlined in the user manual to avoid confusion during reassembly.
Consider a Screw Organizer
If you frequently work with electronic devices, investing in a screw organizer with labeled compartments can be a convenient solution for keeping track of screws.
Double-Check Before Moving On
Before moving on to the next step of disassembly, double-check that you have accounted for all screws and parts. Confirm that they are stored in an organized and easily accessible manner.
Reassess If Necessary
If you encounter unexpected challenges or need to backtrack during the disassembly, reassess the organization of screws and parts to ensure accuracy.
Store in a Safe Location
When taking breaks or completing the disassembly over multiple sessions, store the organized screws and parts in a safe location where they won’t be disturbed or misplaced.
Respect Water Resistance
Respecting water resistance is crucial when working with smart water devices, as these devices are often designed to withstand exposure to water or other liquids. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to respect water resistance during the disassembly process:
Refer to the User Manual
Before starting the disassembly, carefully review the user manual or documentation provided by the manufacturer. Look for information on the device’s water resistance rating and specific guidelines for disassembly.
Identify Water-Resistant Seals
Take note of any gaskets, seals, or rubber components that contribute to the water resistance of the device. These are often located around seams, openings, or connectors.
Use the Right Tools
Ensure that the tools you use are suitable for working with water-resistant devices. Avoid sharp or pointed tools that could damage seals or compromise water resistance.
Inspect for Existing Damage
Before proceeding with the disassembly, inspect the exterior of the device for any existing damage to the water-resistant seals or components. Document any issues you identify.
Power Off and Disconnect
Power off the device and disconnect it from any power sources. This is a standard safety step before disassembly and is especially important for water-resistant devices to avoid electrical hazards.
Be Mindful of Water Entry Points
Identify potential entry points for water, such as ports, buttons, or seams. Take note of these areas and handle them with care during the disassembly process.
Follow Seals Breaking Procedure
If the user manual provides specific instructions for breaking seals, follow those procedures carefully. Breaking seals incorrectly can compromise the water resistance of the device.
Use Antistatic Precautions
If the device contains electronic components, continue to use antistatic precautions to prevent damage to sensitive parts. Ensure that antistatic measures do not compromise water resistance.
Avoid Removing Seals Unnecessarily
Only remove seals or gaskets if necessary for the disassembly process. If a component can be accessed without breaking a seal, leave the seal intact to preserve water resistance.
Protect Openings During Disassembly
As you open the device, be mindful of any open ports or openings. Consider covering them temporarily with clean, lint-free cloths or tape to prevent the entry of dust or debris.
Work in a Controlled Environment
If possible, work in a clean and controlled environment to minimize the risk of introducing contaminants that could compromise water resistance.
Reassess Seals Before Reassembly
Before reassembly, carefully inspect all water-resistant seals, gaskets, and components. Replace any damaged or worn seals to maintain the device’s water resistance.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines for Reassembly
When reassembling the device, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommended procedures for restoring water resistance. This may include applying new seals or using specific adhesives.
Conduct Water Resistance Testing (if applicable)
If the device undergoes water resistance testing after reassembly, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for this process. This step ensures that the device maintains its water-resistant properties.
Document Water Resistance Status
After reassembly, document the status of the device’s water resistance. Note any changes or issues that may need attention.
Consult Professional Help (if unsure)
Consulting professional help is a prudent step if you are uncertain or uncomfortable with any aspect of the disassembly process for a smart water device. Here’s a step-by-step guide on when and how to seek professional assistance:
Assess Your Comfort Level
If you feel uncertain, lack the necessary expertise, or encounter unexpected challenges during the disassembly process, assess your comfort level and acknowledge when professional help may be beneficial.
Review the User Manual
Refer to the user manual or documentation for guidance. Some manufacturers provide troubleshooting tips or contact information for customer support.
Check for Warranty Information
Review the warranty information for the smart water device. Opening the device may void the warranty, and it’s important to consider this before seeking professional help.
Contact Manufacturer Support
Reach out to the manufacturer’s customer support for assistance. They can provide guidance, answer questions, and offer solutions to common issues related to the device.
Visit the Manufacturer’s Website
Check the manufacturer’s official website for online resources, FAQs, or forums where users may share their experiences and solutions. Some manufacturers provide detailed disassembly and troubleshooting guides.
Explore Online Communities
Visit online communities or forums where users discuss similar devices. You may find experienced individuals who can offer advice or solutions based on their own experiences.
Consider Authorized Service Centers:
If the smart water device is under warranty or if you want professional assistance, consider contacting an authorized service center. These centers are equipped to handle repairs and can ensure that the device is serviced by trained technicians.
Professional Repair Services
If you are unable to resolve the issue independently or through manufacturer support, consider seeking professional repair services. There are third-party repair shops or technicians who specialize in electronic devices and may offer assistance.
Avoid Irreversible Actions
If you are unsure about a particular step or action, avoid irreversible actions that could cause permanent damage to the device. Stopping and seeking professional help is a responsible approach.
Check for DIY Repair Services
Some manufacturers or third-party services provide do-it-yourself (DIY) repair kits with instructions for specific issues. Evaluate whether such kits are available and suitable for your situation.
Local Electronics Repair Shops
Explore local electronics repair shops that have experience with water-resistant devices. They may offer insights, guidance, or services to address your specific concerns.
Document the Issue
Document the issue you’re facing, any steps you’ve taken, and any error messages or symptoms observed. This information can be useful when seeking professional assistance.
Consider Legal Implications
Be aware of any legal implications related to device warranties or terms of service. Opening the device may void warranties, and professional assistance may come at a cost.
Prioritize Safety
If there is a risk of personal injury or further damage to the device, prioritize safety and seek professional help immediately.
Reassess the Situation
If the disassembly process becomes more complex than anticipated, reassess the situation and make a well-informed decision on whether to continue independently or seek professional help.
Conclusion
In conclusion, successfully opening smart water devices requires a systematic approach and adherence to key steps. Reading the manual, powering off the device, using the right tools, and prioritizing safety are fundamental initial steps. Identifying seals and latches, documenting the process, and inspecting for damage ensure a meticulous disassembly. Working in a clean area, respecting water resistance, and keeping track of screws and parts contribute to an organized and efficient process. When uncertainties arise, consulting professional help is a wise choice. By following these key steps, you can approach the disassembly of smart water devices with confidence and professionalism, ensuring both safety and success in the task at hand.
